Angles - UnEqual
Angles (unequal)
Dimensional Properties
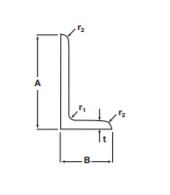
- Mass per unit length (kg/m)
- Width of Sections A and B (mm)
- Thickness of section t (mm): The vertical part connecting two flanges
- Root Radius r1(mm): The fillet radius at the connection of web & flange
- Toe Radius r2(mm): The fillet radius at the end of the section
- Distances of center of gravity(Cx and Cy)
Mechanical Properties
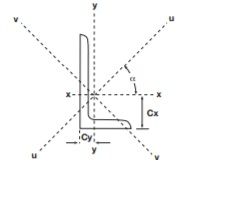
- Second Moment of Area(mm4): A geometrical property of an area which reflects how its points are distributed with regard to an arbitrary axis. We mainly consider about the following two axes only
- About x-x axis
- About y-y axis
- About u-u axis
- About v-v axis
- Radius of Gyration(m): The radial distance to a point which would have a moment of inertia the same as the body`s actual distribution of mass. The moment of inertia is considered about the x-x and y-y axis or v-v axis and u-u axis.
- Elastic section modulus(cm3): It is defined as the ratio of the second moment of area to the distance of the neutral axis to any given fibre. Here, the neutral axis is x-x or y-y.
- Torsional Constant: A geometrical property of a bar`s cross-section which is used to determine the relationship between angle of twist and applied torque. The details of its calculation for angles are given in SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
- Slenderness Coefficient: Two values of the equivalent slenderness coefficient are calculated for each unequal angle. The larger value is based on the major axis elastic section modulus to the toe of the short leg and the lower value is based on the major axis elastic section modulus to the toe of the long leg.
