Coating Weight Designation Systems
Coating Weight [Mass] Designation Systems
Each coated steel sheet product has its own coating weight designation system, which is defined in the appropriate ASTM standard. For example, the most widely used ASTM metallic-coated sheet standard is A653/A653M, which covers hot-dip galvanized products.
One of the coating weight designation systems in this standard uses descriptors such as G60, G90, etc. The “G” means the coating is galvanize (zinc), and the numbers refer to the weight of zinc on the surface of the steel sheet in inch-pound (English/Imperial) units. Taking G90 as an example, the coating weight on one square foot of sheet (total- both-sides of the sheet) shall have a triple spot test (TST) average minimum of 0.90 ounces. If equally applied to both sides of the sheet, there would be a minimum of 0.45 ounces on each square foot of surface.
The other measurement system in widespread use today is the SI [Metric] system.
The conversion from the inch-pound weight1 in ounces per square foot (oz/ft2 ) to the SI mass2, 3 in grams per square metre (g/m2 ) is: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 305 g/m2 To convert from oz/ft2 to g/m2 , multiply by 305 Example: G90 (0.90 oz/ft2 ) = Z275 (275 g/m2 )
If what we are interested in is the coating thickness, why do ASTM standards not use thickness measurements?
The answer is simply that it is difficult to directly measure the thickness accurately and repeatedly. For example, a G90 coating contributes about 1.6 mils (0.0016 inches, or about 42 microns) to the total thickness of the coated sheet. For a coating equally applied to both sides of the sheet, this means there is about 0.0008 inches (21 microns) of zinc on each surface. To accurately determine the thickness of the coating, the coated thickness must be measured, the coating stripped off, and then the steel substrate thickness measured using a gauge capable of accurately reading to the nearest ten-thousandth of an inch. This is extremely difficult to do with good accuracy.
On-line equipment is available that can non-destructively do this (see sidebar), but the most representative manual method of determining the amount of coating present is to measure its weight [mass] on a larger and given surface area using the “weigh-strip-weigh” technique. Weigh-strip-weigh refers to the procedure of weighing a standard size sample of the product using a very accurate scale, stripping the coating in an inhibited acid without removing any of the substrate, then reweighing the coupon to determine the weight [mass] loss. This is the original method of determining coating weight [mass], and, in fact, is still the referee method used to check and calibrate nondestructive on-line and laboratory coating thickness gauges.
There are weigh-strip-weigh procedures that can be used for all zinc-based coatings in commercial production today. For the most common products, these procedures are defined in ASTM 1 Weight is a measure of the pull of the force of gravity (Weight/Force = Mass x Acceleration of gravity) 2 Mass is a fundamental property – the same everywhere 3 For the purpose of measuring metallic coatings, mass and weight are equivalent everywhere on earth COATING WEIGHT MEASUREMENT
There is a very precise on-line technique for measuring coating thickness. The equipment required is expensive, uses sophisticated x-ray or radioisotope fluorescence devices, and requires considerable expertise to operate. These gauges repeatedly sense the coating thickness on each surface, average a large number of readings, and then convert the results to the more familiar coating weight units. Laboratory versions of this equipment are also available.
These gauges require calibration based on weigh-strip-weigh testing. Standard A90/A90M, and cover galvanized and galvannealed sheet, 55% aluminum-zinc alloy-coated sheet, zinc-5% aluminum alloy-coated sheet, and zinc-aluminum-magnesium alloy-coated sheet. There are special procedures required for other types of alloy coatings such as aluminized, and zinc-nickel alloy electroplated sheet. These are covered by other ASTM standards.
ASTM Coating Designations – What do they specify?
- ASTM designations for hot-dip coated sheet specify:
- Minimum triple spot test (TST) value
- Average of three edge-center-edge readings
- A total-both-sides (TBS) requirement (See A924/A924M for testing details)
- Minimum single spot test (SST) value
- Is based on a TST only!
- The TST test only applies to the original, full-width (as-coated) sheet
- Narrow sheet cut from full-width sheet is subject only to a minimum SST, TBS requirement
- With the exception of supplementary Table S2.1 in A653/A653M, ASTM specifications are silent on the minimum weight on one side of a single spot
- Examples of full-width pass/fail test results for A653 are given below
Table 1 Example G90 Coating Weight Results – Illustrating Passing and Failing the Requirements
- of A653/A653M (Table 1) – values in oz/ft2
- Requirements of A653 (Table 1):
- Minimum Triple Spot Test average (TST), Total Both Sides (TBS) – 0.90 oz/ft2
- Minimum Single Spot Test (SST), Total Both Sides (TBS) – 0.80 oz/ft2
- Minimum One Side (OS), Triple Spot Test average (TST) – 0.32 oz/ft2 (per Footnote A of A653 Table 1)
| Example | Test | E1 | E2 | E3 | TST | Comments |
| 1 | TBS | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.94 | Passes min TST |
| 2 | TBS | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.91 | Passes min TST |
| 3 | TBS | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.93 | 0.89 | Passes min TST |
| 4 | TBS | 0.78 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.90 | Passes min TST |
| 5 | OS-Top | 0.30 1 | 0.31 1 | 0.40 | 0.34 | Passes on min TST-OS & TBS |
| OS-Bot | 0.55 | 0.62 | 0.47 | 0.54 | ||
| TBS | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.91 | ||
| 6 | OS-Top | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.31 | Passes on min TST-OS & TBS |
| OS-Bot | 0.55 | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.60 | ||
| TBS | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.91 |
Designation System for Galvanized and Galvannealed Sheet Products
Galvanize – For galvanized sheet, common inch-pound coating weight designations (ordered as A653 or A1063) are, in oz/ft2:
G30 G40 G60 G90 G115
These designations specify the minimum average TST, total-both-sides, tested per ASTM A924/A924M, e.g., G90 requires a minimum average TST of 0.90 oz/ft2 total-both-sides. The specification stipulates that TST samples shall be taken from defined positions at the edge-center-edge of the as-coated sheet.
There are designations for heavier coatings, such as G165 and G210, but these products are used for very specialized applications and are generally not available on thinner gauge sheet.
In SI units (ordered as A653M or A1063M), the comparable coating mass designations for galvanized sheet are, in g/m2:
Z90 Z120 Z180 Z275 Z350
These designations specify the minimum average TST, total-both-sides, tested per A924/A924M, e.g., Z275 requires a minimum average TST of 275 g/m2 total-both-sides.
In 2007 ASTM added the option of ordering single side, single spot test (SST) coating designations to A653/A653M. These are SI designations only (ordered to A653M) and specify the minimum and maximum allowable coating mass per side for any SST. They take the familiar form of automotive coating designations (numeric characters first – signifying a per side requirement). No inch-pound designations are used since single side coatings are traditionally ordered in SI units only. Examples are:
60G 70G 90G
These designations specify the minimum and maximum SST value on each surface, e.g., 60G requires a minimum of 60 g/m2 and a maximum of 110 g/m2 of zinc on each surface for any SST.
When specifying single side single spot coatings, the designation for each surface must be shown, e.g., 60G60G.
Zinc-Iron (Galvanneal) – The common inch-pound coating weight designations (ordered as A653) for galvannealed sheet (zinc-iron alloy-coated) are, in oz/ft2:
A25 A40 A60
As with galvanized product designators, A40 for example, requires a minimum average TST coating weight of 0.40 oz/ft2, total-both-sides. While the coating contains approximately 8 to 10% iron, resulting in the density being slightly higher than a zinc coating and the coating thickness being slightly less than a G40 galvanize coating, the difference is too small to be of concern
The SI equivalent coating mass designations (ordered as A653M) for galvannealed sheet are, in g/m2:
ZF75 ZF120 ZF180
ZF120, for example, requires a minimum average TST of 120 g/m2 total-both-sides.
As with galvanize, the option of ordering zinc-iron coatings to single side, SST coating designations has been added to A653/A653M. Again, these are SI designations only (ordered to A653M), specifying the minimum and maximum allowable coating mass per side for any single spot, and taking the familiar form of automotive coating designations (numeric characters first – signifying a per side requirement). No inchpound designations are used since single side coatings are traditionally ordered in SI units only. Examples are:
45A 50A
These designations relate to the minimum and maximum SST value on each surface, e.g., 45A requires a minimum of 45 g/m2 and a maximum of 75 g/m2 of zinc-iron alloy on each surface for any SST.
When specifying single side, SST coatings, the designation for each surface must be shown, e.g., 45A45A.
For galvanized and galvannealed sheet, the three-significant figure relationship between coating weight [mass] and thickness (based on zinc density of 446 lb/ft3 [7140 kg/m3]) is:
1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00168 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0427 mm
Designation System for Electrogalvanized Sheet Products
For electroplated coatings (pure zinc and zinc-based alloy coatings), SI system (g/m2) designators are most commonly used, although ASTM Standard A879/A879M for electrogalvanize includes the inch-pound [oz/ft2] designator system. The reason for the initial use of SI designators is that many electroplated products were and still are used for automotive applications. Automobile producers, who implemented worldwide coated sheet specifications many years ago, use only SI units.
For electrogalvanized sheet, common inch-pound coating weight designations (ordered as A879) are, in oz/ft2:
08Z 13Z 30Z
These designations relate to the minimum and maximum SST value on each surface, as defined in ASTM A879/A879M, e.g., 13Z requires a minimum of 0.13 and a maximum of 0.23 oz/ft2 of zinc on each surface for any SST. Again, the numeric characters come first, signifying per side requirements.
When specifying, the designation for each surface must be shown, e.g., 13Z13Z.
For electrogalvanized sheet, common SI coating weight designations (ordered as A879M) are, in g/m2:
24G 40G 90G
These designations relate to the minimum and maximum SST value on each surface, as defined in ASTM A879/A879M, e.g., 40G requires a minimum of 40 and a maximum of 90 g/m2 of zinc on each surface for any SST.
Keeping ASTM Designation Systems Straight
As hot-dip galvanized and galvannealed coatings saw more use by the automotive industry, it became the practice to manufacture these products to conform to single side, SST g/m2 values; that being the requirement of automotive manufacturers. Products ordered for construction and other general end uses continue to be ordered to total-both-sides, TST, inch-pound designations. For hot-dip galvanize, as we have seen, ASTM uses “G” (prior to the numerals) in the designator for inch-pound coatings and “Z” for SI coatings – total-both-sides in each case. On the other hand, for electrogalvanize “G” (after the numerals) means SI units and “Z” means inch-pound units – single spot, single side in each case.
The use of both dimensional units, and the reversal of “G” and “Z” between TST hot-dip, and single side, SST EG in ASTM specifications, certainly can lead to confusion in the marketplace. Table 2 below summarizes what the various designations mean in terms of single spot and triple spot requirements.
Table 2 Galvanized Sheet Coating Designations Explained
|
Coating Designation Format |
Product Type and Coating Requirements |
||||||
|
Specification |
Coating |
Units |
Coating Tests Required |
||||
|
Single Side |
Total Both Sides |
||||||
|
SST |
TST |
SST |
TST |
||||
|
Gnn |
A653 – Table 1 |
Zinc - HD |
oz/ft2 |
NONE |
Min |
Min |
Min |
|
Znn |
A653M – Table 1 |
Zinc - HD |
g/m2 |
NONE |
Min |
Min |
Min |
|
Ann |
A653 – Table 1 |
Zinc-iron - HD |
oz/ft2 |
NONE |
Min |
Min |
Min |
|
ZFnn |
A653M – Table 1 |
Zinc-iron - HD |
g/m2 |
NONE |
Min |
Min |
Min |
|
nnZnnZ |
A879 |
Zinc - EG |
oz/ft2 |
Min & Max |
NONE |
NONE |
NONE |
|
nnGnnG |
A879M |
Zinc - EG |
g/m2 |
Min & Max |
NONE |
NONE |
NONE |
|
nnGnnG |
A653 M – Table S2.1 |
Zinc - HD |
g/m2 |
Min & Max |
NONE |
NONE |
NONE |
|
nnAnnA |
A653 M – Table S2.1 |
Zinc-iron - HD |
g/m2 |
Min & Max |
NONE |
NONE |
NONE |
|
nnGnnG |
Auto (typical) 1 |
Zinc - HD & EG |
g/m2 |
Min & Max |
NONE |
NONE |
NONE |
|
nnAnnA |
Auto (typical) 2 |
Zinc-iron - HD & EG |
g/m2 |
Min & Max |
NONE * |
NONE |
NONE |
Notes: nn = numerals (2 or 3) specific to coating weight [mass] HD = Hot-Dip
EG = Electrogalvanize
SST = Single Spot Test
TST = Triple Spot Test
* some auto manufacturers require a minimum TST
For additional clarification, see Table 3 below, which provides the requirements of selected coating weight [mass] examples for galvanized sheet made to ASTM specifications.
It is not easy to keep the terminology straight. Users should be aware that both units are in common use today, and are advised to pay close attention when ordering, knowing precisely what is meant by the terminology being used. See the Table 4 at the end of this article, which summarizesthe designations used for most hot-dip products, and may be useful in keeping terminology clear.
Table 3 Selected ASTM Galvanized Sheet Designations – Requirements
| Product Type | Example Designation | Requirement |
| Hot-Dip Galvanize (A653/A653M) | G90 (A653, Table 1, in-lb) |
TSTa average 0.90 oz/ft2 min – total both sides TST average 0.32 oz/ft2 min – each side SSTb 0.80 oz/ft2 min – total both sides |
| Z275 (A653M, Table 1, SI) |
TST average 275 g/m2 min – total both sides TST average 94 g/m2 min – each side SST 235 g/m2 min – total both sides |
|
| 60G60G (A653M, Table S2.1, SI)c |
SST 60 g/m2 min, 110 g/m2 max – each side | |
| Hot-Dip Galvanneal (A653/A653M) | A40 (A653, Table 1, in-lb) | TST average 0.40 oz/ft2 min – total both sides TST average 0.12 oz/ft2 min – each side SST 0.30 oz/ft2 min – total both sides |
| ZF120 (A653M, Table 1, SI) |
TST average 120 g/m2 min – total both sides TST average 36 g/m2 min – each side SST 90 g/m2 min – total both sides |
| 45A45A (A 53M, Table S2.1, SI) | SST 45 g/m2 min, 75 g/m2 max – each side |
13Z13Z SST 0.13 oz/ft2 min, 0.23 oz/ft2 max – each side Electrogalvanize (A879, Table 1, in-lb) (A879/A879M)
a – Triple Spot Test b – Single Spot Test c – For information purposes, Table S2.1 in A 653M shows inch-pound values for the SI coating designations
Total Both Side TST versus Single Side SST Coatings
Because the ASTM total-both-sides, TST designators allow an uneven split of the coating (one side TST must have at least 40% of the specified minimum SST total-both-sides coating weight), it is not possible to precisely convert them to SST, single side designators since the latter specify exact minimums per surface. It is sometimes useful, however, to provide an approximate conversion based on the total coating thickness on both surfaces.
Figure 1 on the next page is a chart that allows this to be done, both in terms of coating designators and thickness of the total coating. For instance, it can easily be seen that a G60 coating has a minimum totalboth-sides thickness of about 1.0 mil, which is the very close to twice the minimum per side thickness (2 x 12.5 microns) of a 90G90G coating. Remember, however, that a G60 coating is an average of 3 readings (TST) and can have an uneven split of the total coating thickness, while a 90G90G coating must have a minimum of 12.5 microns on each side for any single spot.
Figure 1 is a guideline only for estimating coating thickness in terms of the two systems and is not meant to suggest equivalency. Also, the values shown are specified minimums. Actual coatings are always a few percent thicker in order to guarantee the minimums.
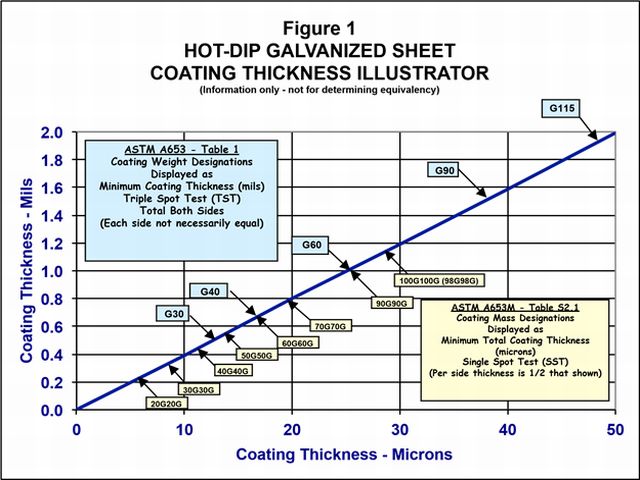
Designation System for 55% Aluminum-Zinc Alloy-Coated Sheet
Steel sheet with a 55% aluminum-zinc alloy coating (55% Al-Zn alloy-coated) is in common use today throughout the construction and appliance industries. It, too, has very specific coating designators. Fortunately, there are only a few designators, but that doesn’t mean there is no confusion about the meaning. The designation systems for coating weight and coating mass are given in ASTM Standard A792/A792M.
The four inch-pound coating weight designations (ordered as A792) are, in oz/ft2:
AZ50 AZ55 AZ60 /span>AZ70
These designations specify the minimum average of a TST, total-both-sides, tested per A924/A924M, e.g., AZ50 requires a minimum average TST of 0.50 oz/ft2 total-both-sides.
These designators are comparable to those used for galvanized sheet in that the dimensions are oz/ft2. Be aware, however, that the designation AZ60 is not equivalent to a G60 coating with respect to the thickness of the coating. Here is where the issue of density comes into play. The coating on 55% Al-Zn alloy coated sheet has 55% aluminum and about 45% zinc. Actually, the coating has a small addition of silicon, but for purposes of this discussion the silicon is not important. Since aluminum is less dense than zinc (a given volume weighs less than the same volume of zinc), an AZ60 coating is thicker than a G60 galvanize coating. See the section on theoretical weight [mass] in GalvInfoNote 1.10 to understand how differences in coating density affect coated sheet.
Because 55% Al-Zn alloy coating and a galvanize coating behave quite differently with respect to corrosion processes, drawing a performance equivalency curve is not possible. There is no answer, therefore, to the question:
What 55% Al-Zn alloy coating is equivalent in performance to a G90 coating? The major use of 55% Al-Zn alloy coated sheet is for construction industry building panels, and for this application the most common coating weights are AZ50 [AZM150] and AZ55 [AZM165]. As the differences in performance between these two designators are subtle, ask your supplier which coating thickness is recommended for your application.
For 55% Al-Zn alloy-coated sheet there is also a SI coating mass designator system (ordered as A792M). The SI equivalents to AZ50, AZ55, AZ60 and AZ70 are, in g/m2:
AZM150 AZM165 AZM180 AZM210
These designations specify the minimum average of a TST, total-both-sides, per A924/A924M, e.g., AZM150 requires a minimum TST of 150 g/m2 total-both-sides.
Since 55% Al-Zn alloy-coated sheet is produced only by the hot-dip process, there is no additional terminology or specification related to the manufacture of an electroplated product. Also, there are no SST, single side designations for this product.
For 55% Al-Zn alloy-coated sheet, the three-significant figure relationship between coating weight [mass] and thickness (based on an alloy density of 234 lb/ft3 [3750 kg/m3]) is:
1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00320 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0813 mm (2)
Designation System for Zinc-5% Aluminum Alloy-Coated Sheet
Steel sheet with a zinc-5% aluminum alloy coating (Zn-5% Al alloy-coated) is used by the construction, automotive, and appliance industries. Zn-5% Al alloy-coated sheet has a coating that consists of 95% zinc and 5% aluminum, and small amounts of other elements to improve processing and product characteristics. The designation systems for coating weight and coating mass are given in ASTM Standard A875/A875M. The common inch-pound coating weight designations (ordered as A875) are, in oz/ft2:
GF30 GF45 GF60 GF75 GF90
These designations specify the minimum average of a TST, total-both-sides, tested per A924/A924M, e.g., GF60 requires a minimum average TST of 0.60 oz/ft2 total-both-sides.
For Zn-5% Al alloy-coated sheet, since the coating contains about 95% zinc, and thus has nearly the same density as zinc, a GF90 coating is approximately equivalent in thickness to a G90 galvanized coating. The equivalent SI coating mass designations (ordered as A875M) are, in g/m2:
ZGF90 ZGF135 ZGF180 ZGF225 ZGF275
These designations specify the minimum average of a TST, total-both-sides, per A924/A924M, e.g., ZGF180 requires a minimum TST of 180 g/m2 total-both-sides.
As with 55% Al-Zn alloy-coated sheet, Zn-5% Al alloy-coated sheet is made only by the hot-dip process so there are no designator systems that involve per side terminology.
For Zn-5% Al alloy-coated sheet, the three-significant figure relationship between coating weight [mass] and thickness (based on an alloy density of 427 lb/ft3 [6840 kg/m3]) is:
1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00175 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0446 mm (3)
Designation System for Zinc-Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy-Coated Sheet
A fourth zinc-based coating that is used where superior corrosion resistance is needed, is zinc-aluminummagnesium alloy-coated (Zn-Al-Mg alloy-coated) sheet. This alloy-coated sheet has 5 coating types, each with different amounts of aluminum and magnesium, as shown below. The designation systems for coating weight and coating mass are given in ASTM Standard A1046/A1046M.
The common inch-pound coating weight designations (ordered as A1046) are, in oz/ft2:
ZM30 ZM40 ZM60 ZM75 ZM90
These designations specify the minimum average of a TST, total-both-sides, tested per A924/A924M, e.g., ZM60 requires a minimum average TST of 0.60 oz/ft2 total-both-sides.
The equivalent SI coating mass designations (ordered as A1046M) are, in g/m2:
ZMM90 ZMM120 ZMM180 ZMM220 ZMM275
As with 55% Al-Zn alloy-coated sheet, Zn-Al-Mg alloy-coated sheet is made only by the hot-dip process so there are no designator systems that involve per side terminology.
For Zn-Al-Mg alloy-coated sheet, the three-significant figure relationship between coating weight [mass] and thickness (based on a density of 375 lb/ft3 [6001 kg/m3] for Type 1, 5-9% Al; 356 lb/ft3 [5700 kg/m3] for Type 1, 9-13% Al; 385 lb/ft3 [6170 kg/m3] for Type 2; 401 lb/ft3 [6430 kg/m3] for Type 3; 415 lb/ft3 [6650 kg/m3] for Type 4; and 388 lb/ft3 [6210 kg/m3] for Type 5) is:
Type 1 – 5 to 9% Al; 2 to 4% Mg: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00200 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0508 mm (4)
> – 9 to 13% Al; 2 to 4% Mg: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00210 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0533 mm (5)
Type 2 – 3 to <5% Al; 2 to 4% Mg: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00195 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0495 mm (6)
Type 3 – 3 to 6% Al; 0.4 to <2% Mg: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00187 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0475 mm (7)
Type 4 – 0.5 to <3% Al; 0.4 to 2.6% Mg: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00181 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0460 mm (8)
Type 5 – 0.5 to 3% Al; 2.6 to 4% Mg: 1.00 oz/ft2 = 0.00193 in = 305 g/m2 = 0.0490 mm (9)
Summary
This article explains the complexities of coating designation systems and hopefully provides a better understanding of why it is important to be sure that you and your supplier are speaking the same language. Table 4 gives examples of some of the designators discussed above.
| Product | Example of Common Coating Designations | Coating Weight inch-pound oz/ft2 | Coating Mass SI g/m2 |
|
| inch-pound | SI | |||
| Total Both Sides - Minimum Triple Spot Average | ||||
| ASTM A653/A653M Galvanize | G90 | Z275 | 0.90 | 275 |
| ASTM A653/A653M Galvanneal | A40 | ZF120 | 0.40 | 120 |
| STM A792/A792M 55% Al-Zn alloy-coated | AZ55 | AZM165 | 0.55 | 165 |
| ASTM A875/A875M Zn-5% Al alloy-coated | GF75 | ZGF225 | 0.75 | 225 |
| ASTM A1046/A1046M Zn-Al-Mg alloy-coated | ZM90 | ZMM275 | 0.90 | 275 |
ASTM A653M
N/A* 60G 0.20 60
Galvanize (Table S2.1)
ASTM A653M N/A* 45A 0.15 45
| ASTM A879/A879M Electrogalvanize |
13Z | 40G | 0.13 | 40 |
| Automotive Specified Galvanize | N/A* | 100G | N/A* | 100 |
| Automotive Specified Galvanneal | N/A* | 45A | N/A* | 45 |
++ Single side designators are used to specify the coating mass for each side and are written, for example, 60G60G, or in the case of differential coating masses, 90G60G.
- https://www.galvinfo.com
