I-Beams
I-Beams
Dimensional Properties
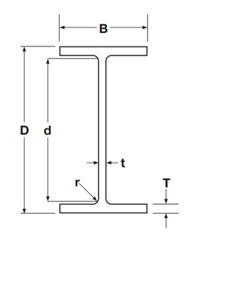
- Mass per unit length (kg/m)
- Depth of the Section D (mm)
- Width of the section B (mm)
- Thickness of Web t (mm): The vertical part connecting two flanges
- Thickness of Flange T(mm): The horizontal section with B>>T
- Root Radius r(mm): The fillet radius at the connection of web & flange
- Depth between the fillets d(mm)
- Ratios of Local Buckling
- Slenderness ratio for flange(B/2T)
- Slenderness ratio for web(d/t)
Mechanical Properties
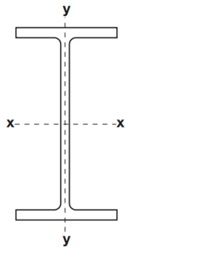
- Second Moment of Area(mm4): A geometrical property of an area which reflects how its points are distributed with regard to an arbitrary axis. We mainly consider about the following two axes only:
- About x-x axis
- About y-y axis
- Radius of Gyration(m): The radial distance to a point which would have a moment of inertia the same as the body`s actual distribution of mass. The moment of inertia is considered about the x-x and y-y axis.
- Elastic section modulus(cm3): It is defined as the ratio of the second moment of area to the distance of the neutral axis to any given fibre. Here, the neutral axis is x-x or y-y.
- Plastic section modulus(cm3): The plastic section modulus depends on the location of the plastic neutral axis (PNA) which is the cross-section splitting axis such that the compression stress equals the tensile stress.
- Buckling Parameter: Dimensionless constant to measure the buckling. To calculate the buckling parameter for I-Beams, please refer to the SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
- Torsional Index: Dimensionless constant to measure the buckling. To calculate the buckling parameter for I-Beams, please refer to the SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
- Warping Constant: The warping constant is required, among other things, for the determination of stresses for the warping torsion as well as for the determination of critical buckling moments for the lateral-torsional buckling analysis. The details of its calculation are given in SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
- Torsional Constant: A geometrical property of a bar`s cross-section which is used to determine the relationship between angle of twist and applied torque. The details of its calculation are given in SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
