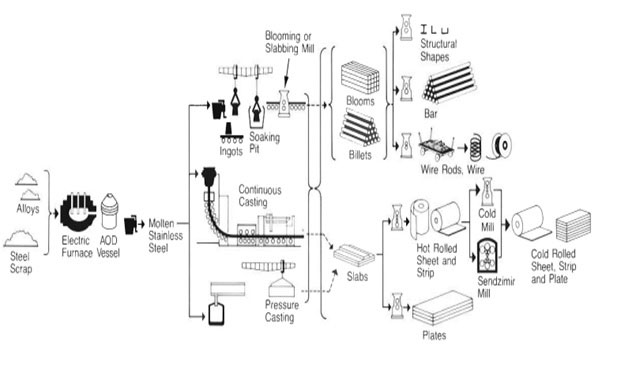
Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing Process
- Stainless steel is produced in an electric arc furnace where carbon electrodes contact recycled stainless scrap and various alloys of chromium.
- A current is passed through the electrode and the temperature increases to a point where the scrap and alloys melt.
- The molten material from the electric furnace is then transferred into an AOD (Argon Oxygen Decarburization) vessel, where the carbon levels are reduced and the final alloy additions are made to achieve the exact chemistry.
- Figure shows the process, which starts with melting and casting into the stainless steel into either ingots or continuous casting into a slab or billet form.
- The material is then hot rolled or forged into its final form. Some material receives cold rolling to further reduce the thickness to create sheet or strip or it is drawn into smaller diameters to make rod and wire.
- Most stainless steels receive a final annealing and pickling.