Manufacturing Process of SAW Pipes
Manufacturing Process of SAW Pipes
- Production of longitudinally welded pipe (U-ing/O-ing process)
The plates employed for longitudinally welded pipe are formed on presses featuring open dies for the U-ing and closed dies for the O-ing operation. There are various stages in the process.
- a. First Stage
In the first forming stage the plate is crimped in the area of its longitudinal edges. The bending radius corresponds roughly to the diameter of the open-seam pipe. Crimping is performed in special forming presses.

Crimping the longitudinal plate edges
- a. First Stage
The plate is bent into a U-shape in one operation involving a circular- radius tool pushing the plate down between two supports. Toward the end of the operation, the distance between the supports is reduced in order to apply a small degree of over bend to counter the spring-back effect.

Forming in the U-ing press
- c. Third Stage
In the third forming stage, the U shape is placed in the O-ing press to produce, in a single operation, the round open-seam pipe. The deformation processes performed in the U-ing and O-ing presses are coordinated so as to ensure that the spring-back effect is effectively countered and the open-seam pipe is as circular as possible with the longitudinal edges flush.
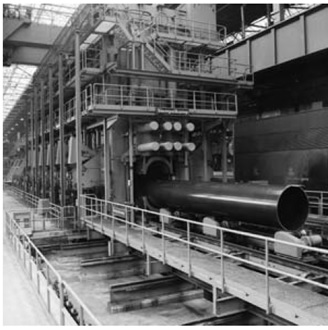
Completion of the open-seam pipe in the O-ing press
The edges of the open-seam pipe are then pressed together (eliminating any offset) in tack-welding stands, which may be designed in the form of roller cages, and then joined by a continuous seam deposited by automatic MAG welders. Depending on the pipe thickness, the welding speed applied can range from 5 to 12 m/min.
The tack-welded pipes are then conveyed by a roller table and distribution system to the submerged-arc welding stands where, at separate lines, they are provided first with the inside and then with the outside pass.These runs are deposited by moving the pipe on a carriage under a stationary welding head. For the inside pass, the welding head is mounted on an arm which extends inside the pipe.In order to preclude the possibility of weld offset, both the inside and outside pass welding heads are continuously monitored and controlled for perfect alignment to the weld centreline.
