Stages of Nonferrous Scrap Recycling Processes
Stages of Nonferrous Recycling Processes
The metal recycling industry has an efficient structure with numerous small companies purchasing scrap material and feeding
this to highly effective larger international businesses.
this to highly effective larger international businesses.
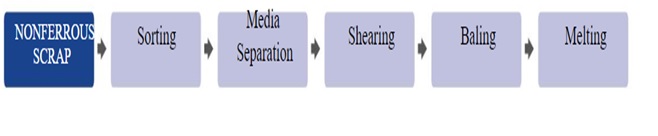
Non-ferrous metal recycling involves some, or all of the following steps:

Feeding recovered copper wire into a conveyor belt for recycling

Baled zinc prepared for transport to a refinery
- Sorting: In order to be recycled appropriately, different types of non-ferrous metals need to be separated from each other, as well as from other recyclables such as paper and plastic.
- Media separation: Shredders incorporate rotating magnetic drums to separate non-ferrous from ferrous metals. Further separation is achieved using electrical currents, high-pressure air flow and liquid floating systems. Further processing may be needed.
- Shearing: Hydraulic machinery capable of exerting enormous pressure is used to cut metals into manageable sizes.
- Baling: Non-ferrous materials are compacted into large blocks to facilitate handling and transportation.
- Melting: The recovered materials are melted down in a furnace, poured into casters and shaped into ingots. These ingots are either used in the foundry industry or they can be transformed into flat sheets and other wrought products such as tubing, which are then used to manufacture new products.
Nonferrous Specifications who processes metals for a living and mention the word Zorba, Honey, Vader, Berry, or Twitch, you’ talking about nonferrous metals like aluminum, copper, lead, and zinc. You’re also talking about combinations, shapes, sources, and chemical compositions to some degree. In 1914, the National Association of Waste Material Dealers began categorizing the different kinds of scrap metals that recyclers were processing to be used by manufacturers.
Many of these transactions were made via teletype messages (like SMS text messages of today) and were charged by the letter. In order t keep the costs down, NAWMD used four- or five-letter code names for various types of nonferrous scrap. Berry, for exam means high quality (No. 1) copper wire that is free of virtually any other metals. Twitch refers to aluminum collected from shredding automobiles that went through a specific process of media separation to ensure a certain level of purity
Nonferrous scrap is then consumed by secondary smelters, refiners, ingot makers, foundries and other industrial consumers in the United States and more than 70 countries worldwide. These consumers rely on nonferrous scrap as a competitive, environmentally-friendly and energy-e input to make brand new products, continuing the n metal life cycle.
The Bureau of International Recycl estimates that almost 40 percent of the world’s dem copper is met using recycled material, while more than 80 percent of the zinc available for recycling is eventually recycled
