T-Beams
T-Beams
Dimensional Properties
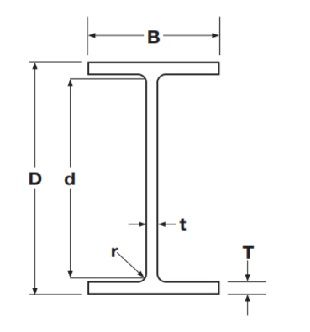
- Mass per unit length (kg/m)
- Depth of the Section D (mm)
- Width of the section B (mm)
- Thickness of Web t (mm): The vertical part connecting two flanges
- Thickness of Flange T(mm): The horizontal section with B>>T
- Root Radius r(mm): The fillet radius at the connection of web & flange
- Depth between the fillets d(mm)
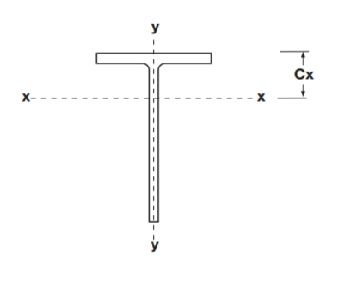
- Cx is Y-coordinate of COM
- Ratios of Local Buckling
- Slenderness ratio for flange(B/2T)
- Slenderness ratio for web(d/t)
Mechanical Properties
- Second Moment of Area(mm4): A geometrical property of an area which reflects how its points are distributed with regard to an arbitrary axis. We mainly consider about the following two axes only:
- About x-x axis
- About y-y axis
- Radius of Gyration(m): The radial distance to a point which would have a moment of inertia the same as the body`s actual distribution of mass. The moment of inertia is considered about the x-x and y-y axis.
- Buckling Parameter: Dimensionless constant to measure the buckling. To calculate the buckling parameter for T-Beams, please refer to the SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
- Torsional Index: Dimensionless constant to measure the buckling. To calculate the buckling parameter for joists, please refer to the SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
- Warping Constant: The warping constant is required, among other things, for the determination of stresses for the warping torsion as well as for the determination of critical buckling moments for the lateral-torsional buckling analysis. The details of its calculation are given in SCI publication P057 Design of members subject to combined bending and torsion
